March 18 (Reuters) – With the U.S. and European banking crisis wreaking havoc in global markets, some financial industry executives are calling on the Federal Reserve to pause its monetary policy tightening for now but be ready to resume raising rates later.
Investors are currently pricing a 60% probability that the Fed will raise rates by 25 basis points on Wednesday, with the remainder betting on no change. Some industry executives said the central bank should prioritize financial stability now.
“Go fast and hard on financial stability; go gradual and slow on price stability,” said Peter Orszag, chief executive of financial advisory at investment bank Lazard Ltd (LAZ.N). Orszag said the Fed should pause but be ready to hike again gradually as the situation develops.
The central bank declined to comment. Fed officials are in their pre-meeting blackout period, during which they are barred from commenting on monetary policy or the economic outlook.
The Fed has rapidly raised interest rates over the past year in a bid to beat back inflation, at a pace not seen since the 1980s. Others have joined in, with the European Central Bank raising rates by 50 basis points earlier this week.
The rapid rise in rates after years of cheap money is rippling through global markets and industry. Two U.S. banks have failed over the past week and others have come under pressure, while Swiss lender Credit Suisse is scrambling to pull together a rescue deal this weekend.
Tumult in the banking sector has roiled asset prices, sending U.S. government bond yields plummeting in the past week, with some investors complaining that massive price swings have made it more difficult to trade. U.S. stocks took a rollercoaster ride, though the S&P 500 managed to close higher on the week despite steep losses in bank shares.
WILD CARD
Some market observers have argued that a sustained pause could fuel worries that consumer prices will rebound.
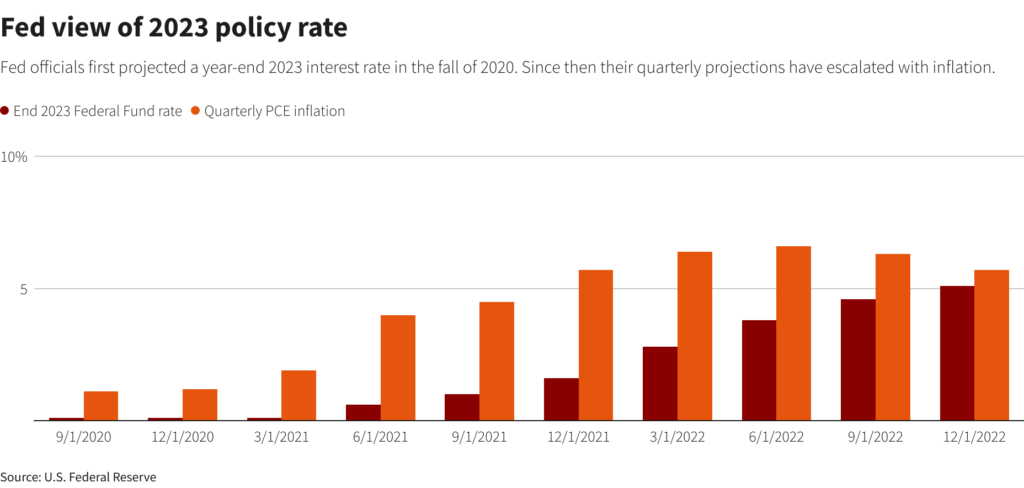
Recent U.S. economic data give the Fed little reason to believe it has defeated inflation. Consumer prices rose at a 6% annual rate in February, nearly three times the central bank’s target, and there have been only nascent signs of a significant easing in hiring and wage growth.
“While the banking woes will certainly command attention, we believe that it is not systemic but more of a liquidity issue that the Fed can contain with its lending facilities,” wrote Bob Schwartz, senior economist at Oxford Economics, in a note.
But he added that the “wild card” will be market reaction.
James Tabacchi, chief executive of broker-dealer South Street Securities, said he thought the Fed would eventually need to go above 6%. The current Fed funds rate is 4.5% to 4.75%.
“I am an inflation hawk. But what will it hurt to wait a month and say, ‘We’d like to see the market stabilize?’” Tabacchi said. “I think the Fed should pause.”
DISINFLATIONARY TRENDS
Orszag, who served as the director of the U.S. Office of Management and Budget in the Obama administration, said as long as long-term inflationary expectations were not unhinged, as was the case now, the Fed had time. Raising rates too rapidly could break things, as the current banking crisis demonstrated.
A number of factors pointed to lingering effects of the pandemic on inflation, such as supply-chain disruptions and demand for travel and entertainment.
In a new paper, Orszag and co-author Robin Brooks, chief economist at the Institute of International Finance, estimated that lagged effects associated with delivery times may explain between 30% and 70% of elevated core PCE inflation in the fourth quarter of 2022. That would work out over time and be a disinflationary force this year, they said.
Torsten Slok, chief economist at Apollo Global Management, wrote in a note on Saturday that the recent tumult in the banking sector is already tightening financial conditions. The events this past week correspond to a 1.5% increase in the Fed funds rate, Slok wrote.
“In other words, over the past week, monetary conditions have tightened to a degree where the risks of a sharper slowdown in the economy have increased,” he said.
BlackRock Inc (BLK.N) strategists argued that the gyrations of the past week showed that markets had woken up to the damage caused by the rapid rise and were pricing in a recession.
“The trade-off for central banks – between fighting inflation and protecting both economic activity and financial stability – is now clear and immediate,” they wrote in a report earlier this week.
Reporting by Paritosh Bansal and Ira Iosebashvili; additional reporting by Dan Burns; Editing by Nick Zieminski
: .